Molecular Biology - bmc.BIOL.B376.001.SP26
Section outline
-
Course Description:
The purpose of this course is to introduce students to molecular biology as a tool used in scientific inquiry. Research scientists increasingly use multiple approaches to address interesting questions. Recent developments in the field of genomics illustrate the emerging need to advance our knowledge of genome organization and gene regulation in order to better understand developmental and cellular processes. In this course, students will learn techniques for nucleic acid manipulation and analysis, and the way these techniques are applied in modern molecular biology. In addition, students will read and critically evaluate primary literature. Students will demonstrate knowledge of the material through written and laboratory work, exams, class discussion and oral presentations.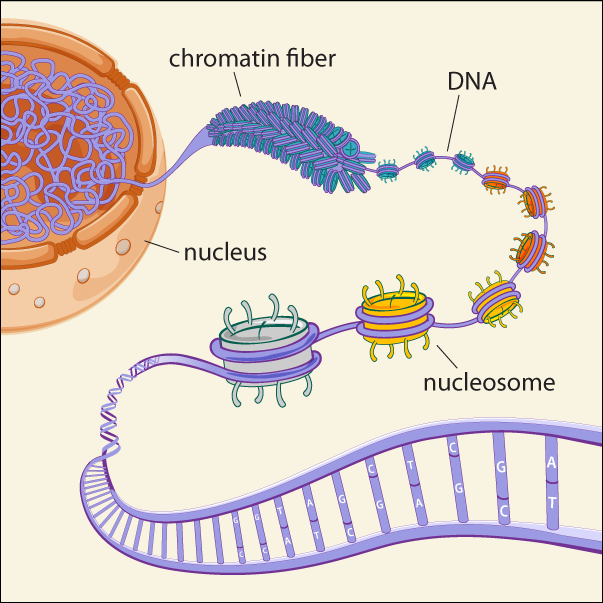
Course learning goals:
- To learn about the structure of the genome and some of the many ways by which gene expression can be regulated.
- To understand and apply basic methodologies used for the manipulation and analysis of nucleic acids.
- To understand how the tools of molecular biology can be used to address biological questions, such as gene cloning based on homology, identification of cis- and trans-acting factors that affect gene expression and gene therapy.
- To read, understand and critically evaluate primary literature.
- To learn scientific writing via the generation of lab reports written in the format of journal articles and a paper reviewing a topic of interest in molecular biology.
- To learn to communicate scientific information orally via presentation of original research conducted in the lab and presentation of a journal article.
Important information about this course:
- Classes will be held in Park Science, room to be determined, MWF from 11:10 am - noon.
- Lab meets in Park Science 126 on Tuesdays from 1:10 - 4 pm.
- Contact info for Dr. Davis - office: Park Science, room 222; e-mail: tdavis@brynmawr.edu; phone: 610-526-5065
- Office hours: tentatively Tuesdays, ~4-5:00 pm (after lab); Wednesdays, noon - 1 pm; by appointment.
- Recommended textbook for the course: Cox, Doudna & O’Donnell, Molecular Biology, Principles and Practice, 2nd edition (ISBN: 978-1-4641-2614-7).
-
57.1 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
408.8 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
Please note that lab WILL meet on Tuesday, January 20th!
-
Course introduction
Nucleic acid structure
DNA manipulation: denaturation & hybridization-
1.8 MB · Uploaded 12/11/25, 13:50
-
-
Amplifying nucleic acids:
PCR & its many applications-
1.3 MB · Uploaded 12/11/25, 14:05
-
93.9 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
223.7 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
-
Recombinant DNA & expression of cloned genes
-
Buck and Axel (1991) A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition, Cell 65: 175-187.
-
247.8 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
-
Genomes: sequencing, structure & composition
Transposable elements-
20.7 MB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
1.2 MB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
Prokaryotic transcription:
RNA polymerase & promoters
Transcription initiation -
Eukaryotic transcription:
Promoters, polymerases & transcription factors -
Eukaryotic transcription: enhancers & activators
check it out -- Dr. Tracy Johnson, the scientist featured at the beginning of Chapter 21, was my roommate in graduate school!-
Shir-Shapira et al. (2015) Structure-Function Analysis of the Drosophila melanogaster Caudal Transcription Factor Provides Insights into Core Promoter-preferential Activation
469.8 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
-
Chromatin structure
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression-
Fraga et al. (2005) Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins
998.8 KB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
Transcription termination
Attenuation in operons & riboswitches-
Mandal et al. (2003) Riboswitches Control Fundamental Biochemical Pathways in Bacillus subtilis and Other Bacteria, Cell 113: 577-586.
-
RNA processing
-
Maunakea et al. (2013) Intragenic DNA methylation modulates alternative splicing by recruiting MeCP2 to promote exon recognition. Cell Research 23: 1256-1269.
1.7 MB · Uploaded 12/5/25, 14:06
-
RNA interference & microRNAs
-
Reinhart et al. (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403: 901-906.
Pasquinelli et al. (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408: 86-89.
-
Nucleic acid editing
recommended readings: Chapter 13, pp. 452-454, 475-478; Chapter 7, pp. 245-248; supplemental readings posted below -
Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression
